Heat of Combustion
Problem: Resonance Stabilization Energy
PURPOSE
The purpose of this investigation is to determine the heats
of combustion of three related compounds.
From these the heats of formation and the resonance stabilization energy
may be calculated.
DISCUSSION
Consider the molecular structural differences in these three
compounds.
1. phthalic
anhydride:

2.
cis-4-cyclohexene-1,2-dicarboxylic anhydride
2.
2.

3. cis-1,2-cyclohexanedicarboxylic anhydride
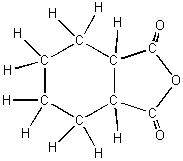
The difference between the heats of
formations of compounds (3) and (2) is the heat of formation of one double
bond. You might expect that the
difference between the heats of formation of compounds (3) and (1) would be
three times that of compounds (3) and (2).
Actually the heat of formation of (1) is less due to the resonance
stabilization energy. The aromatic
nucleus of phthalic anhydride may be written as the
following:
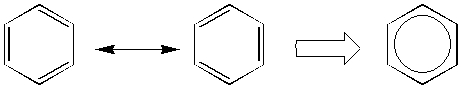
Resonance leads to increased stability
and a lower heat of formation.
DIRECTIONS
Calibrate the calorimeter with benzoic
acid and measure heats of combustion of the acid anhydrides. Remember to use samples no larger than
approximately one gram.
For each anhydride calculate the heat
of combustion, the enthalpy of combustion, and the enthalpy of formation. From the enthalpies of formation determine
the resonance stabilization energy of the aromatic nucleus.
Compare your value with the literature
value of 49 kcal/mol (205 kJ/mol) for benzene and try
to account for any difference.
SAMPLE
CALCULATIONS
Experiment: Bomb Calorimeter 2